Legal notice EU (project) The Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities in partnership with CEEY will design proposals for the design of care systems at level of federal states and of municipalities, which will further support the progress in reducing the inequalities and foster social mobility.
Legal notice EU (project) The Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities in partnership with CEEY will design proposals for the design of care systems at level of federal states and of municipalities, which will further support the progress in reducing the inequalities and foster social mobility.
Context
This project is a follow-up of the research project developed by CEEY and El Colegio de México in the first phase of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities. The results showed the need for structural changes to break the bottlenecks of social mobility and reduce inequality in Mexico.
Based on the above, the new phase of the project focuses on the knowledge base that will inform the setting up of care systems in the states of Guanajuato and Nuevo Leon and in the municipality of San Pedro Garza Garcia.
Guaranteeing the right to care in the Constitution is essential to advance on the basis of social consensus. In order to define the articulation mechanisms in a law, it is necessary to understand the care systems at different levels as transversal and multipurpose policies that are worth discussing collectively, as they imply much more than the already great challenge of expanding the existing infrastructure of services and social spending. The Care Economy also implies creating fiscal strategies to redistribute paid and unpaid work, adapted policies for those who require care and for caregivers, social co-responsibility and co-responsibility of the private sector.
Therefore, it requires more and better statistical information, strengthening surveys and data systems, as well as developing studies to make visible the interdependence of care with multiple agendas, identifying care needs and their characteristics, available supply and unmet demand, allowing for strategic planning and follow-up from the short to the long term, starting with priority groups that include children, people with disabilities, the sick and elderly, and their caregivers.
This project is part of the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities. Coordinated by AFD and financed by the European Commission, the Extension of the Facility will contribute to the development of public policies aimed at reducing inequalities in four countries: South Africa, Mexico, Colombia and Indonesia over the period 2021-2025.
Objectives
Given the above context, the objective of this project is the construction of two products that address two identified needs:
- a design proposal for a state and municipal-level care system: it is necessary to develop a care system designs that address the structural inequalities for which their creation is sought. In this sense, it is necessary to establish a complete, functional and sustainable design.
- a proposal for the collection and systematization of primary information for the design and/or monitoring of the care system: a second need arises from the above in terms of systematization of primary and administrative information that feeds, as far as possible, the original design of the care systems, as well as their monitoring over time.
Research findings
You will find below the research papers related to this project:
- Social mobility, care policies and social protection (August 2024)
- Social mobility, care policies and social protection policies in Nuevo León (September 2024)
Contact
-
Anda DAVID
Economist, scientific coordinator of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities

Discover other research projects
 Legal notice EU (project) What are the distributional effects of green taxes in Mexico and how can they be quantified? The Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities program seeks to answer this in collaboration with RIBOS and the researches of the Laboratorio National de Politicas Publicas (LNPP) to provide to Mexican policymakers and stakeholders timely analyses of the effects of environmental tax policies on inequalities.
Legal notice EU (project) What are the distributional effects of green taxes in Mexico and how can they be quantified? The Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities program seeks to answer this in collaboration with RIBOS and the researches of the Laboratorio National de Politicas Publicas (LNPP) to provide to Mexican policymakers and stakeholders timely analyses of the effects of environmental tax policies on inequalities.
Context
This research project proposes to estimate the distributive effect of gasoline taxes using a fiscal incidence considering these effects in the context of Mexico´s fiscal system, including the principal tax and spending instruments.
In 2014, Mexico’s Finance Ministry (SHCP) introduced a special tax (IEPS) on carbon as a green tax aimed at reducing the green gas emission associated with fossil fuels, mainly gasoline and diesel. However, the tax revenue (4699 million pesos in 2014) and the environmental impact of this tax are marginal: in the past decade, until 2014, this tax had a negative value, thus working as a subsidy. Since that year, it became a tax, which has grown significantly in recent years, representing close to 300 billion pesos in 2019 and 2020. This is therefore in effect by far the most important green tax implemented in Mexico today.
This analysis is of particular interest for Mexico at present because the transition from fuel subsidies to fuel taxes represents in effect the principal tax reform implemented in Mexico over the last decade in terms of both tax revenue (from -300 to +300 billion pesos in tax revenue) and distribution. Gasoline taxes have significant impacts on all the population, both directly on middle- and higher-income households through private transport, but especially indirectly for lower income households through public transport and transport costs for all goods and services, notably food. Preliminary analysis at the Fiscal Policy Equity Lab (FPEL) reveals that the increase in the indirect tax burden for the poor associated to gasoline taxes may reverse the effect poverty-reduction effect of direct transfers, even after their recent expansion.
Quantifying these impacts precisely will allow the design of compensatory instruments to protect the poorest and most vulnerable groups from the regressive effects of these taxes.
This project is part of the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities. Coordinated by AFD and financed by the European Commission, the Extension of the Facility will contribute to the development of public policies aimed at reducing inequalities in four countries: South Africa, Mexico, Colombia and Indonesia over the period 2021-2025.
Objectives
This project is a joint undertaking between RIBOS, CEQ Institute and LNPP. It seeks to estimate the effect of green taxes in the context of the overall Mexican tax system through the international methodology developed by the Commitment to Equity Institute (CEQI), using INEGI data from the Encuesta de Ingresos y Gastos de los Hogares (ENIGH) for 2014-2020, among other data sources.
This methodology will allow an estimation the effect of green taxes in the context of the overall fiscal system. This methodology facilitates comparability in time and space, and generates a wide variety of incidence indicators, including effects on the income Gini coefficient as well as income poverty using national and international poverty lines.
This project ultimately aims to provide Mexican policy makers and stakeholders with timely analyses of the effects of tax policies on inequality and poverty. The research conducted will therefore result in:
- a research paper,
- a policy brief whose analysis is based on the collaborative intelligence technique. Two sessions in which the model calibration and hypotheses will be discussed following the collaborative modeling framework. Participants in the sessions will be members of the expert network and key tax policy makers.
Research findings
You will find below the research paper related to this project:
- Distributive impact of green taxes in Mexico (July 2024)
The policy brief related to this project will be published here soon.
Contact
-
Anda DAVID
Economist, scientific coordinator of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities

Discover other research projects
 Legal notice EU (project) The Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities in partnership with Fedesarrollo and in close collaboration with the Ministry of Finances implemented the methodology of the Commitment to Equity (CEQ) to analyze the country's fiscal structure and its impact on inequalities specially after major changes caused by the Covid 19 pandemic and the fiscal reform passed at the end of 2022.
Legal notice EU (project) The Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities in partnership with Fedesarrollo and in close collaboration with the Ministry of Finances implemented the methodology of the Commitment to Equity (CEQ) to analyze the country's fiscal structure and its impact on inequalities specially after major changes caused by the Covid 19 pandemic and the fiscal reform passed at the end of 2022.
Context
Prior to the pandemic caused by COVID - 19, Colombia had shown positive results with respect to the reduction of poverty and inequality. For example, total poverty was reduced by 6.1 percentage points between 2012 and 2018 from 40.8% to 34.7% as was extreme poverty, which went from 11.7% to 8.2%, according to official statistics. Likewise, although Colombia is among the most unequal countries in the region, it reduced its Gini index by about 0.03 units from 0.539 in 2012 to 0.508 in 2017, according to data from the National Administrative Department of Statistics (Departamento Administrativo Nacional de Estadísticas, 2021).
However, with the public health contingency, many people lost their jobs or had their incomes reduced due to pandemic containment measures that affected both aggregate supply and aggregate demand. Naturally, according to official statistics, poverty levels increased significantly and inequality rebounded to the levels of five years ago. In fact, by 2020, the country was, according to the latest ECLAC Social Panorama, the most unequal in Latin America (Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean, 2021).
In this sense, the country's tax structure plays a fundamental role to the extent that direct, indirect and in-kind transfers are transformed into support for the most vulnerable households so that they can meet their basic needs and balance these inequalities to some extent. In addition, taking into account that progressivity is one of the principles of the tax system, those with higher incomes should pay higher taxes to finance social spending. In this sense, the tax reform that began to take effect in 2018 and now the Fiscal Reform adopted at the end of 2022 made some major modifications to the corresponding statute with the objective of increasing revenues.
This project is part of the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities. Coordinated by AFD and financed by the European Commission, the Extension of the RFI will contribute to the development of public policies aimed at reducing inequalities in four countries: South Africa, Mexico, Colombia and Indonesia over the period 2021-2025.
Objectives
The methodology developed by the Commitment to Equity institute (CEQ) has been used to carry out this study. The CEQ methodology allows to do a fiscal incidence analysis, that is, to analyze the redistributive impact of public policy instruments, on the tax side, as well as on the social spending side, on poverty and inequalities. In this sense, based on household surveys, it is possible to assess the redistributive capacity of taxes and transfers (whether direct or indirect) to guide public policy in this area.
The aim of the study was to identify which policies, either from the tax side or from the expense side, allow a greater impact (negative or positive) on inequalities. This then gives us, and the government, a clearer picture of the effects of the fiscal structure.
In addition, the project sought to build a tool that parameterizes the tax structure and social spending and allows making microsimulations that are useful for policy discussions. In this sense, this project sought to accompany the teams of the Ministry of Economy, providing them with a tool that allows them to carry out the necessary simulations to evaluate the impacts of different policies. The recently adopted tax reform was also analyzed through the lens of this tool.
Research findings
You will find below the research paper related to this project:
Contact
-
Anda DAVID
Economist, scientific coordinator of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities

Discover other research projects
Reducing spatial inequalities through efficient public service delivery in Colombia
Completed
2024 - 2025
 Legal notice EU (project) This research project conducted by the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities in close collaboration with DANE and DNP, and in partnership with Fedesarrollo, conducted a comprehensive analysis of inequalities in Colombia through the implementation of the diagnostic on inequalities. It also aimed, together with DANE, to strengthen statistics on inequalities in the country.
Legal notice EU (project) This research project conducted by the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities in close collaboration with DANE and DNP, and in partnership with Fedesarrollo, conducted a comprehensive analysis of inequalities in Colombia through the implementation of the diagnostic on inequalities. It also aimed, together with DANE, to strengthen statistics on inequalities in the country.
Context
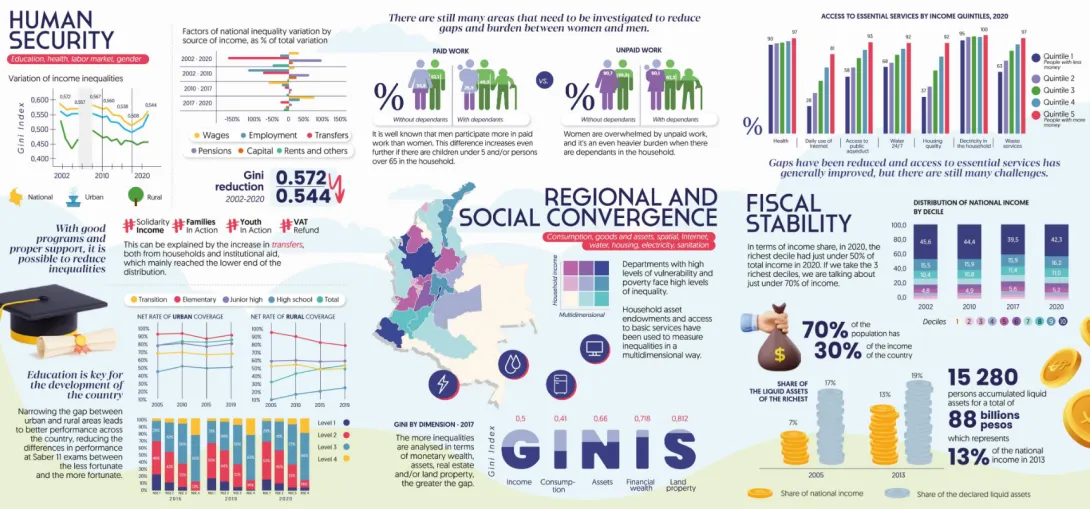
In Colombia, and in other countries, the objective of the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities is to provide analysis, methodologies, and statistics that allow understanding the state of inequalities in the country, the dynamics and interrelationships with the different areas, sectors, and regions of the economy. The objective is to provide robust and updated data, to provide evidence for the construction of public policies, but also to identify areas where data collection can be improved, and those where research can be deepened to better understand the context and support the construction of public policies aimed at reducing inequalities...
In Colombia, DANE has made great progress in recent years in the collection and availability of data in order to analyze and better understand the reality of the country. Several studies have been carried out with some of these data, but, for several years, there has been no comprehensive analysis of inequalities at the national level using several databases to get a complete picture of the country's situation. Since mid-2021, AFD has been working hand-in-hand with DANE and Fedesarrollo to carry out a multidimensional diagnostic on inequalities, based on an innovative reference methodology created by AFD. It provides a comprehensive view of the country's situation as it covers a wide range of aspects (health, education, incomes, etc.) all under the prism of inequalities and using different indicators and databases.
This project is framed in a context in which inequalities acquire crucial relevance in the public policy of the current government and in the agreements adopted by it within the framework of the 2030 agenda, as well as in its entry into the OECD.
This project is part of the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities. Coordinated by AFD and financed by the European Commission, the Extension of the Facility will contribute to the development of public policies aimed at reducing inequalities in four countries: South Africa, Mexico, Colombia and Indonesia over the period 2021-2025.
Objectives
The project aimed to support and strengthen the production of national statistics on inequalities, promoting exchanges and interoperability between DANE and other national and international institutions. More specifically, the main objectives were:
- To implement the methodology of the multidimensional diagnostic on inequalities, and therefore create the first national diagnostic on inequalities in Colombia. For this, AFD worked hand in hand with Fedesarrollo and in close collaboration with DANE.
- To accompany DANE's technical teams in the production, updating and improvement of statistics on inequalities based on the inequality diagnostic methodology. These data will be used to monitor over time the evolution of the indicators considered relevant, and, depending on the outcome of the data collected, to advance in analyses that integrate elements related to climate change and the environment.
- To support DANE’s technical teams in implementing new methodologies and initiatives to obtain statistics that allow a better understanding of the distribution of income of individuals and households in the country. Workshops and seminars served to share experiences and establish practices that allow high-quality data for decision-making.
Find out more about the methodology
Research findings
The research project led to the publication of the multidimensional diagnostic on inequalities in Colombia. It takes into account multiple dimensions of inequality: income distribution, consumption, labour income, household assets and services, level of wealth in land and financial assets, access to and quality of education and health, access to basic services... This document is key to understanding the gaps that exist in Colombia, and allows for evidence-based decision-making and progress towards reducing inequalities.
To go further
Contact
-
Anda DAVID
Economist, scientific coordinator of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities

For further reading on inequalities
Discover other research projects
Analysis of Colombia’s fiscal policy and public spending impact on inequalities
Completed
2022 - 2023
Reducing spatial inequalities through efficient public service delivery in Colombia
Completed
2024 - 2025