Goal 10 calls on countries to adapt policies and legislation to increase the income share of the poorest 40% and to reduce wage inequalities based on gender, age, disability, social or ethnic origin, or religion. This includes promoting greater representation of developing countries in global decision-making.
 © AFD
© AFD
 Legal notice EU (project) What are the distributional effects of green taxes in Mexico and how can they be quantified? The Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities program seeks to answer this in collaboration with RIBOS and the researches of the Laboratorio National de Politicas Publicas (LNPP) to provide to Mexican policymakers and stakeholders timely analyses of the effects of environmental tax policies on inequalities.
Legal notice EU (project) What are the distributional effects of green taxes in Mexico and how can they be quantified? The Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities program seeks to answer this in collaboration with RIBOS and the researches of the Laboratorio National de Politicas Publicas (LNPP) to provide to Mexican policymakers and stakeholders timely analyses of the effects of environmental tax policies on inequalities.
Context
This research project proposes to estimate the distributive effect of gasoline taxes using a fiscal incidence considering these effects in the context of Mexico´s fiscal system, including the principal tax and spending instruments.
In 2014, Mexico’s Finance Ministry (SHCP) introduced a special tax (IEPS) on carbon as a green tax aimed at reducing the green gas emission associated with fossil fuels, mainly gasoline and diesel. However, the tax revenue (4699 million pesos in 2014) and the environmental impact of this tax are marginal: in the past decade, until 2014, this tax had a negative value, thus working as a subsidy. Since that year, it became a tax, which has grown significantly in recent years, representing close to 300 billion pesos in 2019 and 2020. This is therefore in effect by far the most important green tax implemented in Mexico today.
This analysis is of particular interest for Mexico at present because the transition from fuel subsidies to fuel taxes represents in effect the principal tax reform implemented in Mexico over the last decade in terms of both tax revenue (from -300 to +300 billion pesos in tax revenue) and distribution. Gasoline taxes have significant impacts on all the population, both directly on middle- and higher-income households through private transport, but especially indirectly for lower income households through public transport and transport costs for all goods and services, notably food. Preliminary analysis at the Fiscal Policy Equity Lab (FPEL) reveals that the increase in the indirect tax burden for the poor associated to gasoline taxes may reverse the effect poverty-reduction effect of direct transfers, even after their recent expansion.
Quantifying these impacts precisely will allow the design of compensatory instruments to protect the poorest and most vulnerable groups from the regressive effects of these taxes.
This project is part of the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities. Coordinated by AFD and financed by the European Commission, the Extension of the Facility will contribute to the development of public policies aimed at reducing inequalities in four countries: South Africa, Mexico, Colombia and Indonesia over the period 2021-2025.
Objectives
This project is a joint undertaking between RIBOS, CEQ Institute and LNPP. It seeks to estimate the effect of green taxes in the context of the overall Mexican tax system through the international methodology developed by the Commitment to Equity Institute (CEQI), using INEGI data from the Encuesta de Ingresos y Gastos de los Hogares (ENIGH) for 2014-2020, among other data sources.
This methodology will allow an estimation the effect of green taxes in the context of the overall fiscal system. This methodology facilitates comparability in time and space, and generates a wide variety of incidence indicators, including effects on the income Gini coefficient as well as income poverty using national and international poverty lines.
This project ultimately aims to provide Mexican policy makers and stakeholders with timely analyses of the effects of tax policies on inequality and poverty. The research conducted will therefore result in:
- a research paper,
- a policy brief whose analysis is based on the collaborative intelligence technique. Two sessions in which the model calibration and hypotheses will be discussed following the collaborative modeling framework. Participants in the sessions will be members of the expert network and key tax policy makers.
Research findings
You will find below the research paper related to this project:
- Distributive impact of green taxes in Mexico (July 2024)
The policy brief related to this project will be published here soon.
Contact
-
Anda DAVID
Economist, scientific coordinator of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities

Discover other research projects
 Legal notice EU (project) The Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities in partnership with Fedesarrollo and in close collaboration with the Ministry of Finances implemented the methodology of the Commitment to Equity (CEQ) to analyze the country's fiscal structure and its impact on inequalities specially after major changes caused by the Covid 19 pandemic and the fiscal reform passed at the end of 2022.
Legal notice EU (project) The Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities in partnership with Fedesarrollo and in close collaboration with the Ministry of Finances implemented the methodology of the Commitment to Equity (CEQ) to analyze the country's fiscal structure and its impact on inequalities specially after major changes caused by the Covid 19 pandemic and the fiscal reform passed at the end of 2022.
Context
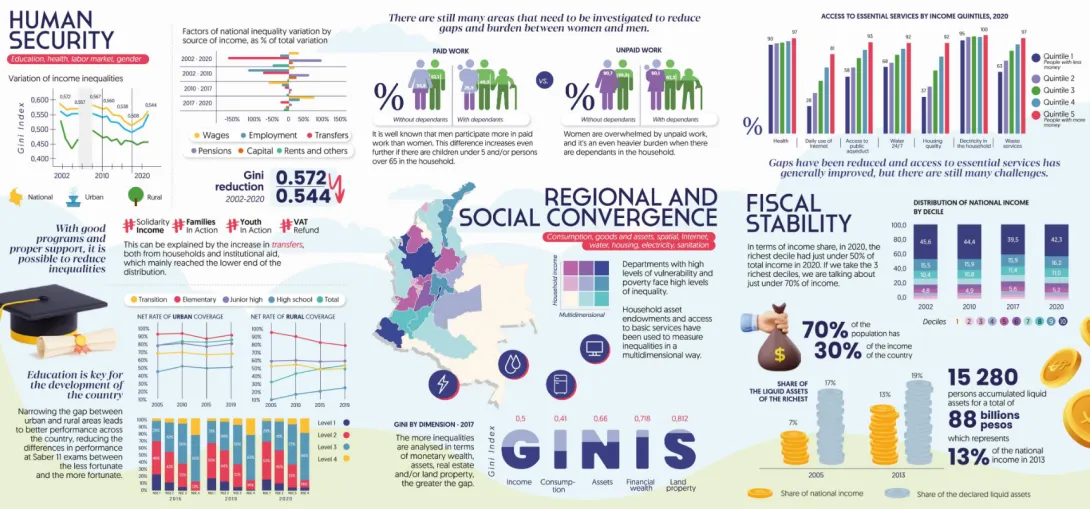
Prior to the pandemic caused by COVID - 19, Colombia had shown positive results with respect to the reduction of poverty and inequality. For example, total poverty was reduced by 6.1 percentage points between 2012 and 2018 from 40.8% to 34.7% as was extreme poverty, which went from 11.7% to 8.2%, according to official statistics. Likewise, although Colombia is among the most unequal countries in the region, it reduced its Gini index by about 0.03 units from 0.539 in 2012 to 0.508 in 2017, according to data from the National Administrative Department of Statistics (Departamento Administrativo Nacional de Estadísticas, 2021).
However, with the public health contingency, many people lost their jobs or had their incomes reduced due to pandemic containment measures that affected both aggregate supply and aggregate demand. Naturally, according to official statistics, poverty levels increased significantly and inequality rebounded to the levels of five years ago. In fact, by 2020, the country was, according to the latest ECLAC Social Panorama, the most unequal in Latin America (Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean, 2021).
In this sense, the country's tax structure plays a fundamental role to the extent that direct, indirect and in-kind transfers are transformed into support for the most vulnerable households so that they can meet their basic needs and balance these inequalities to some extent. In addition, taking into account that progressivity is one of the principles of the tax system, those with higher incomes should pay higher taxes to finance social spending. In this sense, the tax reform that began to take effect in 2018 and now the Fiscal Reform adopted at the end of 2022 made some major modifications to the corresponding statute with the objective of increasing revenues.
This project is part of the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities. Coordinated by AFD and financed by the European Commission, the Extension of the RFI will contribute to the development of public policies aimed at reducing inequalities in four countries: South Africa, Mexico, Colombia and Indonesia over the period 2021-2025.
Objectives
The methodology developed by the Commitment to Equity institute (CEQ) has been used to carry out this study. The CEQ methodology allows to do a fiscal incidence analysis, that is, to analyze the redistributive impact of public policy instruments, on the tax side, as well as on the social spending side, on poverty and inequalities. In this sense, based on household surveys, it is possible to assess the redistributive capacity of taxes and transfers (whether direct or indirect) to guide public policy in this area.
The aim of the study was to identify which policies, either from the tax side or from the expense side, allow a greater impact (negative or positive) on inequalities. This then gives us, and the government, a clearer picture of the effects of the fiscal structure.
In addition, the project sought to build a tool that parameterizes the tax structure and social spending and allows making microsimulations that are useful for policy discussions. In this sense, this project sought to accompany the teams of the Ministry of Economy, providing them with a tool that allows them to carry out the necessary simulations to evaluate the impacts of different policies. The recently adopted tax reform was also analyzed through the lens of this tool.
Research findings
You will find below the research paper related to this project:
Contact
-
Anda DAVID
Economist, scientific coordinator of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities

Discover other research projects
Reducing spatial inequalities through efficient public service delivery in Colombia
Completed
2024 - 2025
 Legal notice EU (project) This research project conducted by the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities in close collaboration with DANE and DNP, and in partnership with Fedesarrollo, conducted a comprehensive analysis of inequalities in Colombia through the implementation of the diagnostic on inequalities. It also aimed, together with DANE, to strengthen statistics on inequalities in the country.
Legal notice EU (project) This research project conducted by the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities in close collaboration with DANE and DNP, and in partnership with Fedesarrollo, conducted a comprehensive analysis of inequalities in Colombia through the implementation of the diagnostic on inequalities. It also aimed, together with DANE, to strengthen statistics on inequalities in the country.
Context
In Colombia, and in other countries, the objective of the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities is to provide analysis, methodologies, and statistics that allow understanding the state of inequalities in the country, the dynamics and interrelationships with the different areas, sectors, and regions of the economy. The objective is to provide robust and updated data, to provide evidence for the construction of public policies, but also to identify areas where data collection can be improved, and those where research can be deepened to better understand the context and support the construction of public policies aimed at reducing inequalities...
In Colombia, DANE has made great progress in recent years in the collection and availability of data in order to analyze and better understand the reality of the country. Several studies have been carried out with some of these data, but, for several years, there has been no comprehensive analysis of inequalities at the national level using several databases to get a complete picture of the country's situation. Since mid-2021, AFD has been working hand-in-hand with DANE and Fedesarrollo to carry out a multidimensional diagnostic on inequalities, based on an innovative reference methodology created by AFD. It provides a comprehensive view of the country's situation as it covers a wide range of aspects (health, education, incomes, etc.) all under the prism of inequalities and using different indicators and databases.
This project is framed in a context in which inequalities acquire crucial relevance in the public policy of the current government and in the agreements adopted by it within the framework of the 2030 agenda, as well as in its entry into the OECD.
This project is part of the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities. Coordinated by AFD and financed by the European Commission, the Extension of the Facility will contribute to the development of public policies aimed at reducing inequalities in four countries: South Africa, Mexico, Colombia and Indonesia over the period 2021-2025.
Objectives
The project aimed to support and strengthen the production of national statistics on inequalities, promoting exchanges and interoperability between DANE and other national and international institutions. More specifically, the main objectives were:
- To implement the methodology of the multidimensional diagnostic on inequalities, and therefore create the first national diagnostic on inequalities in Colombia. For this, AFD worked hand in hand with Fedesarrollo and in close collaboration with DANE.
- To accompany DANE's technical teams in the production, updating and improvement of statistics on inequalities based on the inequality diagnostic methodology. These data will be used to monitor over time the evolution of the indicators considered relevant, and, depending on the outcome of the data collected, to advance in analyses that integrate elements related to climate change and the environment.
- To support DANE’s technical teams in implementing new methodologies and initiatives to obtain statistics that allow a better understanding of the distribution of income of individuals and households in the country. Workshops and seminars served to share experiences and establish practices that allow high-quality data for decision-making.
Find out more about the methodology
Research findings
The research project led to the publication of the multidimensional diagnostic on inequalities in Colombia. It takes into account multiple dimensions of inequality: income distribution, consumption, labour income, household assets and services, level of wealth in land and financial assets, access to and quality of education and health, access to basic services... This document is key to understanding the gaps that exist in Colombia, and allows for evidence-based decision-making and progress towards reducing inequalities.
To go further
Contact
-
Anda DAVID
Economist, scientific coordinator of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities

For further reading on inequalities
Discover other research projects
Analysis of Colombia’s fiscal policy and public spending impact on inequalities
Completed
2022 - 2023
Reducing spatial inequalities through efficient public service delivery in Colombia
Completed
2024 - 2025
 Legal notice EU (project) What have been the local stimulus effects of the South African Presidential Employment Stimulus Initiative (PES) and the national social grants program? The Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities in partnership with SALDRU will seek to answer this question.
Legal notice EU (project) What have been the local stimulus effects of the South African Presidential Employment Stimulus Initiative (PES) and the national social grants program? The Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities in partnership with SALDRU will seek to answer this question.
Context
The Covid-19 pandemic has forced societies around the world to make difficult trade-offs, as they try respond to the public health crisis on one hand, and to the economic and social distress arising out of it on the other. In South Africa, these combined crises have exacerbated already high levels of unemployment, deepening poverty and heightening levels of hunger and food insecurity.
To mitigate the combined health, social and economic crises stemming from the Covid pandemic, South African President Cyril Ramaphosa announced, in April 2020, a range of support measures to mitigate their impact, including emergency social protection and employment stimulus measures.
This project is part of the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities. Coordinated by AFD and financed by the European Commission, the Extension of the Facility will contribute to the development of public policies aimed at reducing inequalities in four countries: South Africa, Mexico, Colombia and Indonesia over the period 2021-2025.
Objectives
This research project aims to study the local stimulus effects of South Africa's PES and national social grants program. In order to do so, it brings together a wide range of existing and new data sources, such as shopper data provided by Shoprite Checkers and programme participant data from Harambee Youth Employment Accelerator, which are securely merged while preserving individual anonymity using local tech company Omnisient’s proprietary encryption technology.
The primary research focus will be on the multiplier effects of these two programs, that is, the effects of the programs on the economy beyond the direct impact of spending on program participants and their households.
These program-specific multiplier effects are crucial to the overall evaluation of the programs, particularly in the context of budget constraints, but are difficult to identify in a credible empirical manner given the lack of work on them in South Africa.
In studying them, this project thus has the dual objective of characterizing the spending patterns of stimulus beneficiaries and then examining how such spending is likely to stimulate economic activity in industries further up the product supply chain. Much of the analysis proposed is descriptive and extrapolative rather than causal when it comes to quantifying multiplier effects.
Thus, the overall goal of this research is to provide an incomplete but conservative and credible quantitative baseline for thinking about program-specific multipliers in South Africa, in an environment where such evidence is lacking.
Research findings
The publications and webinars related to this research project are available below.
You will find below the two research papers related to this project:
The project also organized two research conferences to present the results of the research. The replays are available below.
- SALDRU-AFD-EU Event: The stimulus effects of South Africa’s Basic Education Employment Initiative (February 7, 2024)
AFD, the EU Delegation in South Africa and SALDRU hosted a public event on the stimulus effects of the Presidential Youth Employment Initiative – Basic Education Employment Initiative (PYEI-BEEI) at the University of Cape Town.
The PYEI-BEEI programme, which targets 18-35 year-olds eligible as education assistants or general school assistants, is the largest component of South Africa’s Presidential Employment Stimulus (PES), announced in 2020 as one of the support measures against the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The research was presented by Joshua Budlender (one of the project's researchers) and complemented by a presentation on the direct returns to learners in the classroom from the PES interns in the schools. Also under consideration is, as the PYEI-BEEI researchers conclude, whether other public spending (such as social grants) may have similar initial stimulus effects.
An interview with Josh Budlender is also available below:
- Research Conversations: Stimulus effects of public employment programmes (12 June 2024)
A webinar on the stimulus effects of public employment programmes with Anda David (AFD), Ihsaan Bassier (UCT-SALDRU) and Maikel Lieuw-Kie-Song (ILO) was also held.
Download the research papers
Contact
-
Anda DAVID
Economist, scientific coordinator of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities

Discover other research projects
 Legal notice EU (project) Does the use of stimulus programs and social grants by beneficiaries have an impact on the South African economy? Conducted by Infusion Knowledge as part of the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities, this research project examined the purchasing habits of stimulus beneficiaries and analyzed how the new "post-stimulus" environment impacts the trade and decision-making of commercial entities and some of their customers.
Legal notice EU (project) Does the use of stimulus programs and social grants by beneficiaries have an impact on the South African economy? Conducted by Infusion Knowledge as part of the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities, this research project examined the purchasing habits of stimulus beneficiaries and analyzed how the new "post-stimulus" environment impacts the trade and decision-making of commercial entities and some of their customers.
Context
In July 2019, Infusion Knowledge Hub conducted a study on opportunities for wholesale in Stock Road in Philippi in the Western Cape Province on behalf of a large South African supermarket chain. The purpose of the study was to understand the trading environment in the informal and small business market to elicit a value-added cash and carry shopping proposition (Vawda, Prinsloo and Prinsloo, 2019).
In June 2022, as part of a research program launched by the Presidency of South Africa and Agence Française de Développement, funded by the European Union, Infusion Knowledge Hub replicated the study to determine whether there are shifts in purchasing behaviour amongst the informal and small traders that participated in the 2019 research. In doing so, the study aimed to provide granular data on shifts in the informal and small traders’ operating environment around Stock Road in Philippi between July 2019 and June 2022. In addition, the research investigated the spending patterns of 30 Social Relief Distress (SRD) grant recipients and 31 Basic Education Employment Initiative (BEEI) participants.
This project is part of the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities. Coordinated by AFD and financed by the European Commission, the Extension of the Facility will contribute to the development of public policies aimed at reducing inequalities in four countries: South Africa, Mexico, Colombia and Indonesia over the period 2021-2025.
Objectives
This new research project aimed to contribute to the body of knowledge on the impact of social protection and employment stimulus measures on the formal and informal economies.
Two studies analysing the local effects of the South African Presidential Employment Stimulus Initiative (PES) and the national social grants programme were produced:
- One study, presented in note form, that builds on Infusion's long-standing relationship with Shoprite to allow SALDRU to use Shoprite's customer data to explore the shopping habits of stimulus beneficiaries. The focus was on unpacking purchasing data related to beneficiaries who receive the Distressed Social Relief Grant and those who are part of the school assistants programme managed by the Department of Basic Education (DBE).
- A research paper that details through descriptive and inferential statistical analysis the transfer to a mobile application, called NECTA, of a landmark study by Infusion and Shoprite conducted among informal vendors and "Spaza" stores in Philippi. This data provides an overview of what has been happening in these businesses since July 2019 (the date of the initial project), as well as an opportunity to see how the new "post-stimulus" environment is impacting the trade and decision-making of these business entities as well as some of their customers.
Research findings
You will find below the research paper related to this project:
Contact
-
Anda DAVID
Economist, scientific coordinator of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities

Discover other research projects
Redesigning the South African “Social Relief Distress” grant program for higher impact
Completed
2023 - 2023
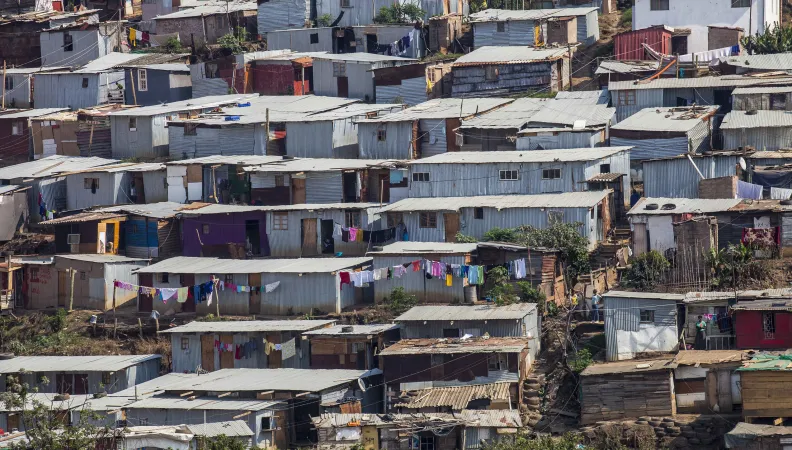 How can we better understand local realities and more particularly socio-economic outcomes at the community level? The Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities in partnership with the Southern Africa Labour and Development Research Unit (University of Cape Town), and in close collaboration with local and national government entities, seeks to answer this question.
How can we better understand local realities and more particularly socio-economic outcomes at the community level? The Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities in partnership with the Southern Africa Labour and Development Research Unit (University of Cape Town), and in close collaboration with local and national government entities, seeks to answer this question.
Context
South Africa’s spatial inequality translates in significantly different lived experiences among members of different communities across the country. Statistics South Africa gathers data on a range of socio-economic outcomes of individuals and households through an array of national surveys; these data can be analysed at the national, provincial, district and sometimes municipal level, and provide us with a sense of well-being, deprivation and inequities in these, between these different geographies. However, there is not yet one standardised set of data that would allow for a coherent, systematic and longer-term understanding, visualisation and tracking of a broad set of indicators on well-being, that allows for a better understanding of socio-economic outcomes at the community level. Yet, understanding this local context is important, as it is within that local reality that policies and interventions aim to make a difference. South Africa’s government has recognised this too and, with the introduction of its District Development (DD) Model, aims to see different spheres and departments of government work together for larger impact, “higher performance and accountability for coherent service delivery and development outcomes”. A consolidated, central point of information that is accurate and regularly updated, would provide a strong basis for the implementation South Africa’s DD Model.
This project therefore proposes the development of an interactive, online Community Explorer that would allow researchers, policy-makers and civil society members to build a stronger understanding of well-being at the community (or main area) level in South Africa. Such an understanding is crucial to inform development efforts implemented at that community level. We suggest drawing on the local level information for the Steve Tshwete municipality to pilot the Community Explorer approach.
The local municipality of Steve Tshwete is part of the Mpumalanga province, an area that is home to one of the country's largest coal mining areas and accounts for 83% of the coal produced in South Africa. Steve Tshwete can be considered as one of the commercial centers of this province, with one of the largest local economies in the district dominated by the mining, manufacturing and financial sectors. As such, coal mining and the three coal-fired power plants currently in operation are by far the largest contributor to local employment, accounting for 40% of it.
This project is part of the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities. Coordinated by AFD and financed by the European Commission, the Extension of the Research Facility will contribute to the development of public policies aimed at reducing inequalities in four countries: South Africa, Mexico, Colombia and Indonesia over the period 2021-2025.
Objectives
This project proposes to leverage the data and tools already available on the South African Youth Explorer (and the related WaziMap tool). The SA Youth Explorer is a SALDRU-led project that constructs and maps a range of indicators that measure key dimensions of well-being among young people, at various geographical levels. Using Census 2011 data, these indicators are currently constructed for the following domains: demographics, education, living environment, economic opportunities and youth poverty (including income poverty and multidimensional deprivation). In addition, the project has begun the construction, verification and maintenance of a central database of service provision, that allows for government-provided services to be mapped down to the main area level. Finally, it is the project’s aim to explore the possibilities of adding a third layer of knowledge with local labour market demand side information. As such, the overall aim of the proposed project is to provide “an understanding of the functionings of geographical areas as economic and social systems” and thereby “to promote the construction of an integrated and effective” approach to policy and planning that would ultimately contribute to the social betterment of all.
In addition, the project will use the administrative South African Revenue Service (SARS) and National Treasury (NT) Firm-Level (SARS-NT) Panel data developed as a joint SARS–National Treasury–UNU-WIDER initiative which gives matched employee-employer level information and thus allows computing labor market demand indicators. The greatest advantage of the administrative SARS–NT Panel data over other firm-level surveys is that it allows us to have employee-related information such as income, age and gender, as well as firm-level information such as labour costs, gross sales, industry sector, firm age, productivity, firm size, learnership and training cost . Another advantage of the administrative SARS–NT Panel data which is important for the project is that the worker and firm information can be aggregated to four different geographical levels, namely: province, district municipality, local municipality, and main place . With these geographical levels, it is possible to create local averages of various worker and firm variables that can then be mapped alongside Higher Education Institutes present at the local level.
Research findings
You will find below the two research papers related to this project:
- Developing a Youth Labour Market Index for South Africa at the sub-national level
- Youth and the just transition. A profile of young NEET in Mpumalanga
Contact
-
Anda DAVID
Economist, scientific coordinator of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities

Discover other research projects
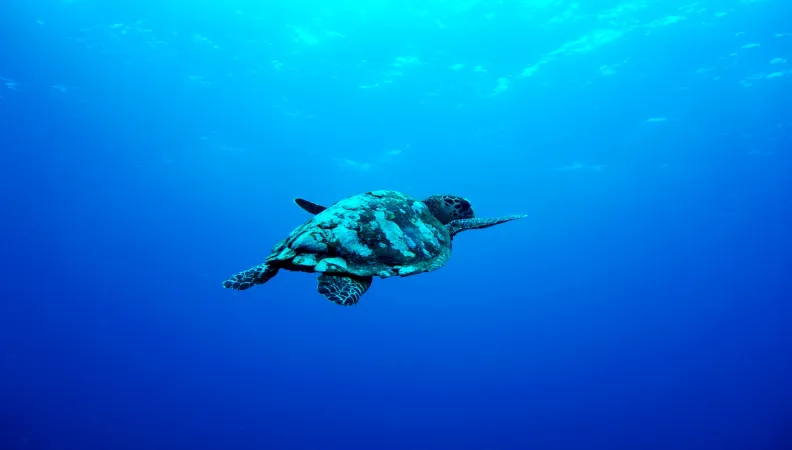 Legal notice EU (project) How do inequalities influence biological and social outcomes in MPAs in Indonesia? The Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities program sought to answer this question in collaboration with SMERU to integrate inequality assessments and indicators into existing MPA policies in the country at all levels of governance.
Legal notice EU (project) How do inequalities influence biological and social outcomes in MPAs in Indonesia? The Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities program sought to answer this question in collaboration with SMERU to integrate inequality assessments and indicators into existing MPA policies in the country at all levels of governance.
Context
MPAs are often associated with high poverty, being by design targeted at relatively untouched areas with low economic potential. Establishing an MPA can thus create a financial and social burden on resource-dependent communities, even if the benefits of doing so would bring higher yields or revenue in the future. Some stakeholders may benefit greatly from commercial activities (e.g., tourism, sale of higher-value products), while at the same time others are left out of the management processes, sometimes even those having most at stake.
Because MPAs will most likely affect user groups disproportionately, inequality issues among stakeholders can easily arise. Some aspects of MPA design, implementation, and management may contribute to positive ecological and well-being outcomes, while others will require tradeoffs. This coexistence of both co-benefits and trade-offs among stakeholder groups leads to tricky questions of equity, justice, and power in the design, implementation, and management of MPAs. There is a general lack of knowledge regarding how inequalities influence MPA outcomes.
In brief, MPAs are a driver of inequalities in communities that rely heavily on marine resources, and a powerful tool to help reduce them. While being an important aspect of the well-being of the people involved and of the success of MPAs, inequality assessments and metrics are currently largely absent in the design, implementation and management of MPAs. This research project aimed at a deeper understanding of the inequality dynamics in MPAs in Indonesia, drawing upon existing data and specific case studies. It helped us gain better knowledge of how inequalities influence biological and social outcomes in MPAs, and brought insights on how to integrate inequality assessments and indicators in existing MPA policies in the country, at every level of governance.
This project is part of the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities. Coordinated by AFD and financed by the European Commission, the Extension of the Facility contributes to the development of public policies aimed at reducing inequalities in four countries: South Africa, Mexico, Colombia and Indonesia over the period 2021-2025.
Objectives & results
This project first went through a scoping phase which enabled to better understand the role of MPAs and its link to inequalities. It then aimed to develop a framework for analyzing inequalities and their dynamics in MPAs in Indonesia, and a toolbox for mainstreaming inequalities in the design, implementation and management of MPAs. It has also fed into the policy dialogue conducted by the EU and AFD on marine resource management and environmental protection.
This project therefore resulted in:
- A working paper summarizing the current knowledge on marine protected areas and inequalities in Indonesia (carried out by LPEM).
- An in-depth research project on the links between inequality reductions and the management of marine protected areas, including cases studies of three MPAs (performed by the SMERU Institute).
- Training and capacity building activities with practitioners and MPA managers on the inclusion of inequalities in MPA management practices.
Research findings
You will find below the different publications related to this project :
- The benefits of Marine Protected Areas in fighting inequality and fostering environmental sustainability in Indonesia
- Balancing conservation and community welfare: Enhancing the management of Marine Protected Areas in Indonesia
- Can social inclusion benefit ecosystems?
Watch the replay of the "Research Conversations" webinar on this topic (July 2023):
Contacts
-
Oskar LECUYER
Research Officer, Environmental Economist

Other research projects supported by the Extension in Indonesia
 Legal notice EU (project) How to effectively reduce inequality in Indonesia? To answer this question, the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities is working with the local research center LPEM and the national statistical office BPS to produce a diagnosis that is essential to guide policy interventions towards reducing inequalities.
Legal notice EU (project) How to effectively reduce inequality in Indonesia? To answer this question, the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities is working with the local research center LPEM and the national statistical office BPS to produce a diagnosis that is essential to guide policy interventions towards reducing inequalities.
Context
In Indonesia, poverty has been declined since 2006 from 17.75% to 9.41% in 2019 due to strong economic growth and other poverty reduction efforts. The inequality, however, remains considerably high. Since 2010, Indonesia’s Gini ratio remains above 0.38. The poverty and inequality situation has been worsen post-pandemic. Indonesia’s headcount poverty rate back to double digit, 10.14% in 2021, while the Gini ratio climbed to 0.384, its highest rate since 2018. While focus on economic inequality is important, the picture of inequality in Indonesia should be assessed through a multi-dimensional aspect, not limited to households income or expenditure.
Indonesia is a fourth most-populous and also the largest archipelagic country in the world. It makes any policy context should be assessed carefully throughout population groups, income class, and geographical location due to the difference in the provision of public infrastructure and policy efforts within the country. As such, a comprehensive inequality diagnostic report is needed to assess overall condition of inequality in Indonesia not only using monetary indicator (income or expenditure), but also social assets, in terms of access to education, health, water and sanitation, employment, and other basic infrastructures needed for households.
The Extension of the Research Facility on Inequalities will cooperate with leading research center, LPEM FEB UI, and national statistical office, BPS, to conduct comprehensive inequality assessment and produce an inequality diagnostic report as the basis for launching a national dialogue about inequality and stimulate policy interventions to overcome inequality.
This project is part of the Extension of the EU-AFD Research Facility on Inequalities . Coordinated by AFD and financed by the European Commission, the Extension of the Facility will contribute to the development of public policies aimed at reducing inequalities in four countries: South Africa, Mexico, Colombia and Indonesia over the period 2021-2025.
Objectives
The objectives of the Inequality Diagnostic Research in Indonesia are:
- to produce a working paper which will consolidate data and resources (papers) around inequality issues to profile the prevailing situation of inequality in Indonesia.
- to conduct capacity building activities for national research center and the national statistical office in performing data analysis for the Inequality Diagnostic Research Report.
- to introduce specific tools for multidimensional inequalities diagnostic in Indonesia.
This research has led to a comprehensive Inequality Diagnostic Research Report in Indonesia and contributes to public debate and discussion on Inequality in Indonesia. Indeed, this project performed a thorough analysis of multi-dimensional aspect of inequality in Indonesia and a comprehensive breakdown based on income groups, geographical locations, and gender. It also includes analysis of prior policies that have been taken by the government to reduce inequality and how it performs overtime. The output of this research will help government to identify priorities and policy options in order to further reduce them.
Research findings
You will find below the research publications related to this project:
Read the press release
Contacts
-
Oskar LECUYER
Research Officer, Environmental Economist

Other research projects supported by the Extension in Indonesia
Harnessing the benefits of inequalities reduction in marine protected areas in Indonesia
Completed
2022 - 2023